A CT scan, also called X-ray computed tomography (X-ray CT) or computerized axial tomography scan (CAT scan), makes use of computer-processed combinations of many X-ray images taken from different angles to produce cross-sectional (tomographic) images (virtual ‘slices’) of specific areas of a scanned object, allowing the user to see inside the object without cutting.
Since its introduction in the 1970s, CT has become an important tool in medical imaging to supplement X-rays and medical ultrasonography. It has more recently been used for preventive medicine or screening for disease.
- Heart Disease
- CT Colonography
Frequently Asked Questions
What should I expect?
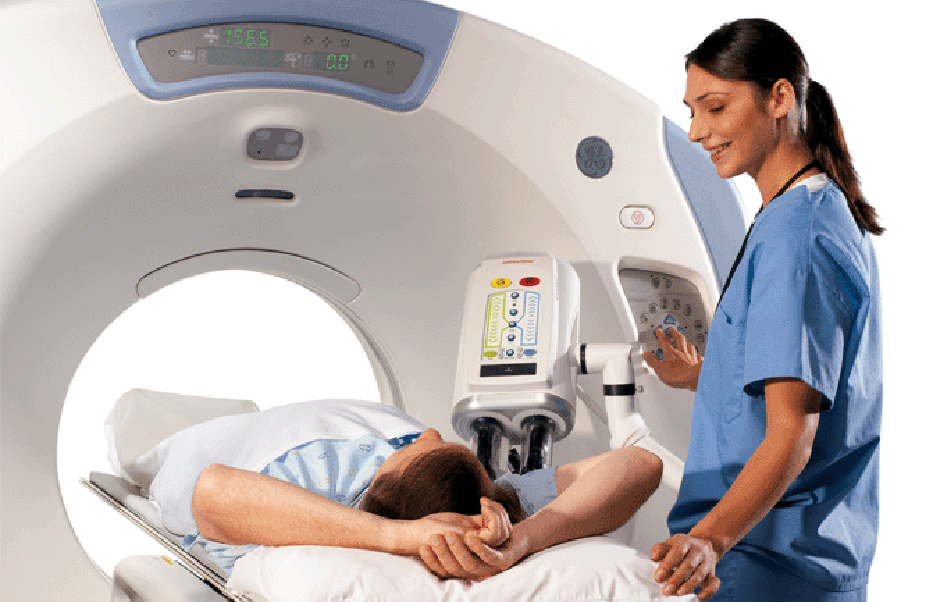
A technologist will escort you into the CT scanning room, where you’ll see a table and a large, donut-shaped device called a gantry. The technologist will have you lie on the padded table and make sure that you’re comfortable. You’ll be asked to lie very still during the scan and hold your breath for a short time to minimize any body movement. During the scan, you might hear a humming or buzzing noise, but you should not feel anything unusual. You may feel the table move while images are being taken at certain locations of your body. The technologist will monitor you during the entire exam through a window and will communicate with you through an intercom. The specific details of your upcoming examination will be explained fully by a CT technologist or your physician..
How long will the exam take?
The actual scan portion of the exam takes only a few seconds. You will be asked to stay still and hold your breath as the CT scanner acquires the X-ray images of your body. Depending on the specific exam, the entire exam may take up to 20 minutes.
Are IVs or shots involved?
Depending on the exam, a solution called “contrast” may be administered with an IV to help improve the accuracy of the examination. Because of this, it is very important to let your doctor know beforehand if you’ve ever had an allergic reaction to contrast, or if you have any other allergies, especially an allergy to iodine-based products.
After the CT exam
A physician will carefully analyze your CT images, review the findings with your physician, and provide a report. Your physician will then discuss
Safety of CT examinations
CT is a safe and effective diagnostic procedure. In fact, nearly 50 million CT exams are performed in the U.S. every year. Like many other imaging technologies, CT has been cleared by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
The profession is supported by the American Registry of Radiology Technologists (ARRT), which provides continuing education, certification and a registry of radiologic technologists. Our health-care professionals involved in your care are professionals who can safely operate the CT scanner and obtain the best images to assist your doctor in making an accurate diagnosis.
Reasons for CT scans
CT exams are performed when people are ill or injured, or when a doctor suspects a medical problem that cannot be detected easily with a routine physical examination. If you have any questions concerning your exam, please talk to your physician or the CT technologist